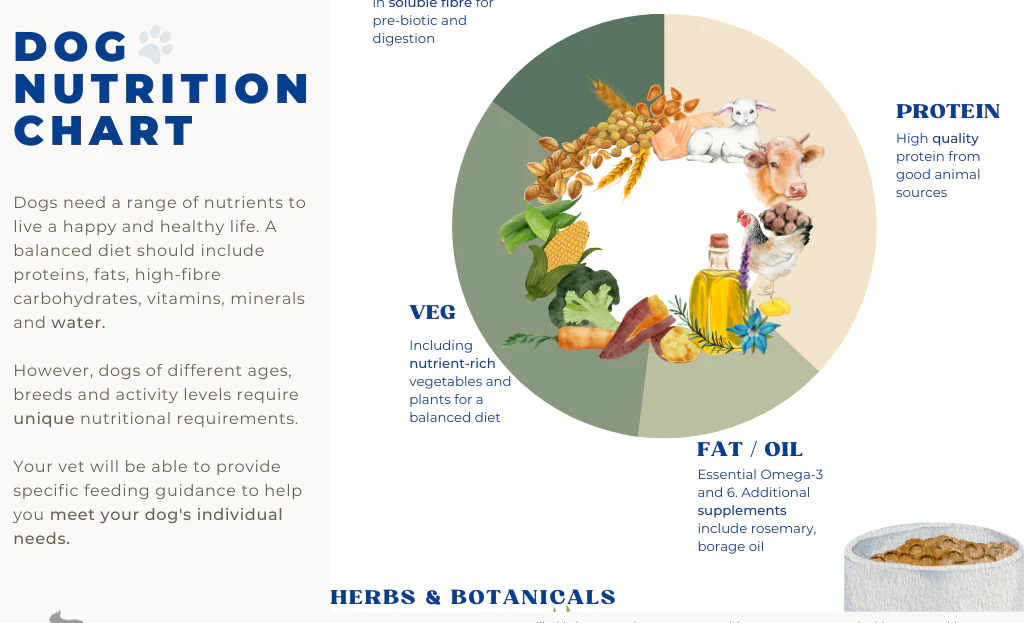
Nutrition plays a vital role in maintaining the health and well-being of dogs. In this article, we’ll explore the essential components of canine nutrition, including key nutrients, dietary needs for different life stages, common dietary issues, and tips for ensuring your dog receives a balanced and nutritious diet.

Key Components of Canine Nutrition
Macronutrients
Dogs require three main macronutrients in their diet:
- Proteins: Essential for muscle growth, repair, and overall body function. Sources include meat, fish, eggs, and legumes.
- Fats: Provide energy, support skin and coat health, and aid in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. Found in oils, animal fats, and fatty fish.
- Carbohydrates: Serve as a source of energy. Common sources include grains (e.g., rice, oats), vegetables, and fruits.
Micronutrients
Vitamins and minerals are crucial for various bodily functions:
- Vitamins: Play roles in immune function, vision, metabolism, and more. Examples include vitamin A, vitamin D, vitamin E, and B vitamins.
- Minerals: Essential for bone health, nerve function, and overall cellular processes. Important minerals include calcium, phosphorus, iron, and zinc.
Dietary Needs for Different Life Stages
Puppies
Growing puppies require a diet rich in calories, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals to support rapid growth and development.
Adult Dogs
Adult dogs need a balanced diet to maintain optimal body condition, energy levels, and overall health.
Senior Dogs
Senior dogs may benefit from diets lower in calories but higher in joint-supporting nutrients like glucosamine and chondroitin.
Common Dietary Issues in Dogs
Food Allergies and Sensitivities
Some dogs may develop allergies or sensitivities to certain proteins (e.g., chicken, beef) or grains (e.g., wheat, corn).
Obesity
Overfeeding and lack of exercise can lead to obesity, which increases the risk of various health problems such as diabetes and joint issues.
Digestive Issues
Digestive upset, including diarrhea or vomiting, may result from dietary changes, food intolerances, or inappropriate feeding practices.
Tips for Ensuring a Balanced Diet for Your Dog
High-Quality Dog Food
Choose dog food formulated to meet the nutritional standards set by organizations like the Association of American Feed Control Officials (AAFCO).
Read Labels
Check ingredient labels to ensure the food contains high-quality proteins, fats, and essential vitamins and minerals.
Portion Control
Follow feeding guidelines based on your dog’s age, size, activity level, and health status to prevent overfeeding or underfeeding.
Fresh Water
Provide clean, fresh water at all times to support digestion, hydration, and overall health.
Homemade vs. Commercial Dog Food
Consider the pros and cons of homemade and commercial dog food options:
- Homemade: Allows you to control ingredients; however, it requires careful formulation to meet nutritional needs.
- Commercial: Convenient and formulated to meet AAFCO standards; choose reputable brands with high-quality ingredients.
Conclusion
Understanding canine nutrition is essential for providing your dog with a healthy and balanced diet. By focusing on key nutrients, meeting dietary needs for different life stages, addressing common dietary issues, and following practical feeding tips, you can ensure your dog receives the nutrition necessary for a happy and healthy life.